如何使用 Python 實現 LRU Cache 快取置換機制

前言
由於電腦記憶體空間(memory)的限制,無法容納所有資料和文件,所以當有新的文件要被置換進入快取(cache)時,必須根據一定的規則來取代掉適合的文件,這就是所謂的快取文件置換機制。
一般來說常見的快取文件置換機制有:
- FIFO(First In, First Out)先進先出算法
- LFU(Least Frequently Used)最近最不常使用算法
- LRU(Least Recently Used)最近最少使用算法
- NMRU(Not Most Recently Used)非最近使用算法
通常我們評量快取機制的指標主要有兩種:延遲(latency)和命中率(hit rate),其中延遲指的是命中後回傳對應資料的所花的時間。而命中率則是需要的資料在快取中被找到的頻率。
本文則要介紹 LRU(Least Recently Used)這個常見經典算法(在 memcached 也有使用),並使用 Python 實現簡單的 LRU 算法。其核心思想主要就是如果資料最近有被使用過,則未來被使用的機率也比較高。實際上的實作基本概念就是快取一定的資料量,若是超過一定的資料量則把最近最少使用的資料淘汰掉。
LRU 基本原理
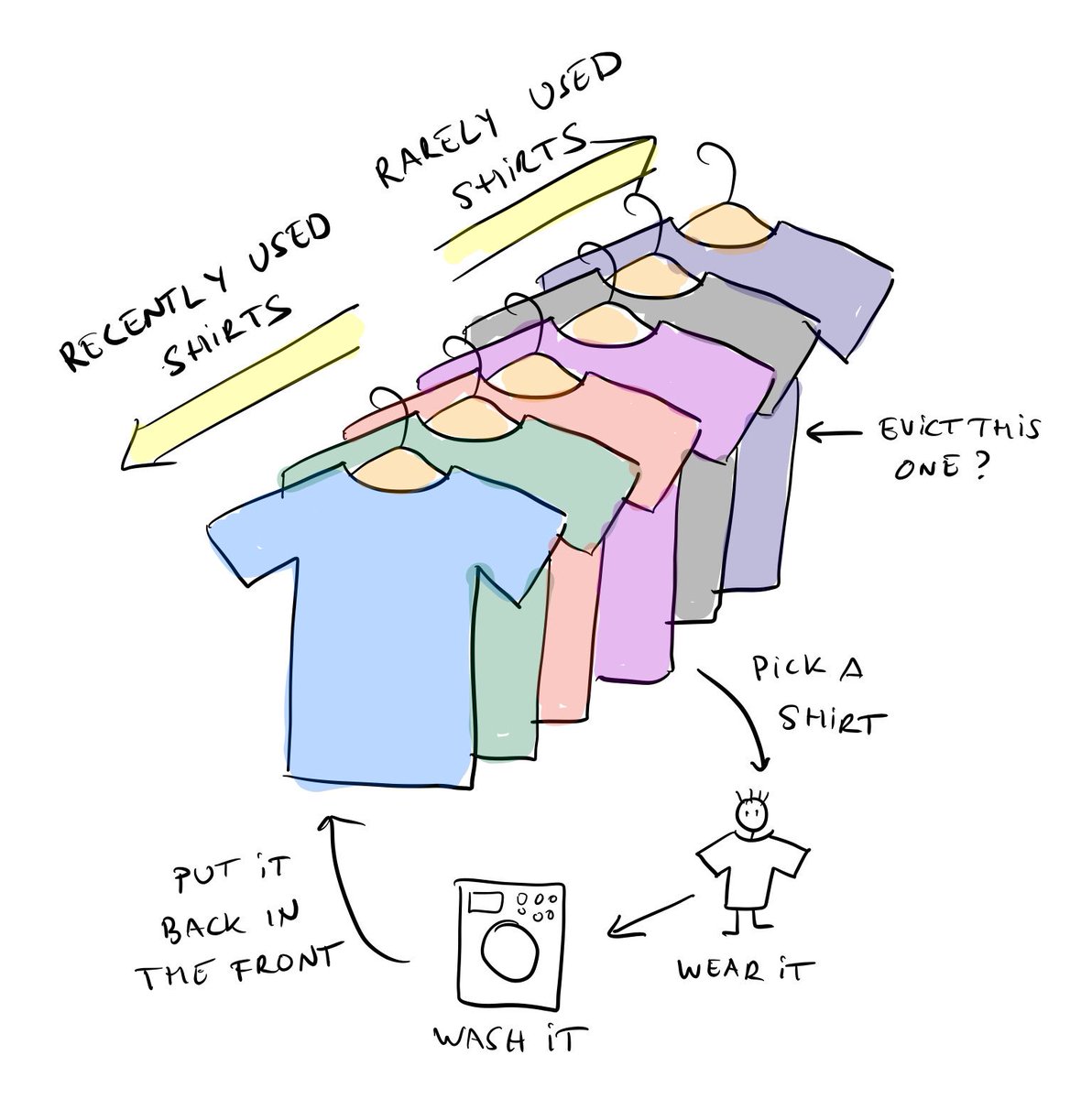
關於 LRU 算法用生活化一點說明就像是平常衣架管理衣服一樣。想像你的衣架是一個有限空間的衣架,越常穿的衣服靠外面。當我們有新衣服時會先從前面放入,要穿衣服時則會把想要的衣服拿出來使用,洗完後放到最前面(因為比較常穿)。當衣服太多超過衣架可容納空間時,最後面不常穿的衣服從衣架掉下去,消失不見:P
使用 Python 實現 LRU 快取方案
通常我們常會使用 hash map 搭配 Double Linked List 來實作(set/get 時間複雜度 O(1)),這樣可以避免單純使用陣列並存 counter/timestamp 的方式需要不停維護 counter 或是只使用 Linked List 實作,在 get 值時時間複雜度為 O(n),來的合適。
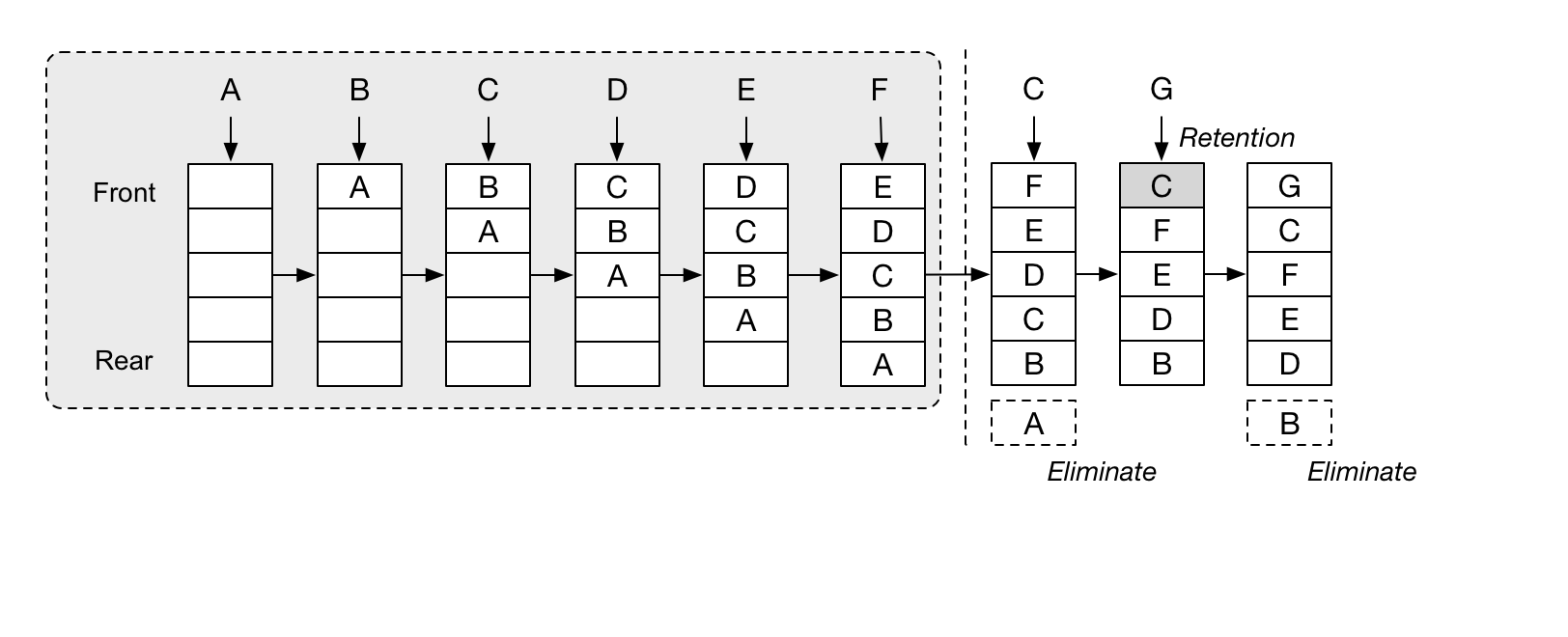
以下我們使用 Python Dict (hash map) 和 Queue (Double Linked List) 來實作簡單的 LRU 算法。
建立一個給定大小的 LRU cache 系統,並實作兩種操作方式,取值和設定值
- get(key):當 key 對應的值存在 cache 系統中時回傳該值,並把該值放到 cache 系統最前面,若沒有對應值則回傳 -1
- set(key, value):當 key 不存在 cache 系統中時,則將 key, value 放入 cache,若系統值滿則移除最不常使用的 key, value 並塞入插入新的 key, value
1 | from collections import deque |
總結
以上簡單介紹如何使用 Python 實現 LRU 快取方案,若是讀者有興趣的話可以自己嘗試 OrderedDict 實作或是針對 multi thread 進行 cache 讀寫操作設計,甚至可以模仿 redis 或 memcached 給儲存資料追加 expire time,實作一個(自幹輪子)更完整的 cache 系統解決方案!
參考文件
(image via twimg、topjavatutorial、Hacker Noon )
關於作者:
@kdchang 文藝型開發者,夢想是做出人們想用的產品和辦一所心目中理想的學校。A Starter & Maker. JavaScript, Python & Arduino/Android lover.:)

留言討論